Introduction
Web 1.0 which came into being in the 1990s was the internet’s basic information retrieval system. Web 2.0 and web 3.0 refer to its future forms or iterations.
The commonly used term web refers to World Wide Web. This WWW initial was supposedly one of the first characters written in a browser while carrying out a search for some particular resource online. This term was coined by Tim Berner Lee (the pioneer of the internet) to refer to the universal web of information that was interconnected via hyperlinked texts.
This article is centered around understanding web 3.0, its comparison to the other versions of the web i.e. web 1.0 and web 2.0 as well as the relevance of web 3.0 in the times to come in different contexts.
1. Understanding web 1.0, web 2.0 and web 3.0

a. Web 1.0
Web 1.0 belongs to the very first stage of the evolution of the World Wide Web. In this time, the number of content creators was limited and the consumers of the content were huge in number. The time span of web 1.0 lasted from around 1991 to 2004 roughly.
Three technologies written by Berner Lee were fundamental to its foundation. These technologies included HTML, URL, and HTTP.
The static webpages which have almost lost their glory these days were the highlight of the era of web 1.0. This was an age when people felt fascinated by features like email and real-time news retrieval etc. Interactive applications were not prevalent at this time but were introduced later through online banking, trading, etc. and content creation was in its very early stages.
b. Web 2.0
The term Web 2.0 gained popularity after the first web 2.0 conference was held by Tim O’Reilly and dale Dougherty. The major features of web 2.0 websites include user-generated content, interaction, and usability for users. The participative social web is another term used for web 2.0.
Web 2.0 is an advanced version of web 1.0 such that the technical specifications remain the same but the way web pages are designed and used enhances the experience of the users.
Web 2.0 has made it possible for millions of users to access user-generated content in seconds. This surge in reach has led to a manifold increase in the generation of such content.
Innovations like mobile internet access and social networks have led to the immense growth of web 2.0. Due to such developments, applications that facilitate user interactivity such as Facebook, Twitter, Airbnb, Instagram, WhatsApp, Youtube, etc. have gained unprecedented importance in our lives and grown into multi-million dollar businesses.
Gig economy also experienced a boost because of these applications, by opening avenues of making money and growing financially to millions of people
Web 2.0 has definitely caused massive disruption to the industries which have failed to follow and adapt to this web-based business model.
c. Web 3.0
Web 3.0 refers to the next evolutionary phase of the web and stands for decentralization, more freedom and utility for the user. It is going to be equally or more disruptive and bring sweeping changes in the way the world operates just like the introduction of web 2.0 did overtime.
Berners Lee used the term ‘Semantic Web’ in a paper in 2001 and represented his vision to bring structure to the content of the web pages by enabling the computers to reliably process the semantic language and carry out many useful tasks for users.
Although web 3.0 doesnot really symbolize this ‘semantic web’ because understanding human language with all its intricate nuances and layers by a computer is not easy to achieve.
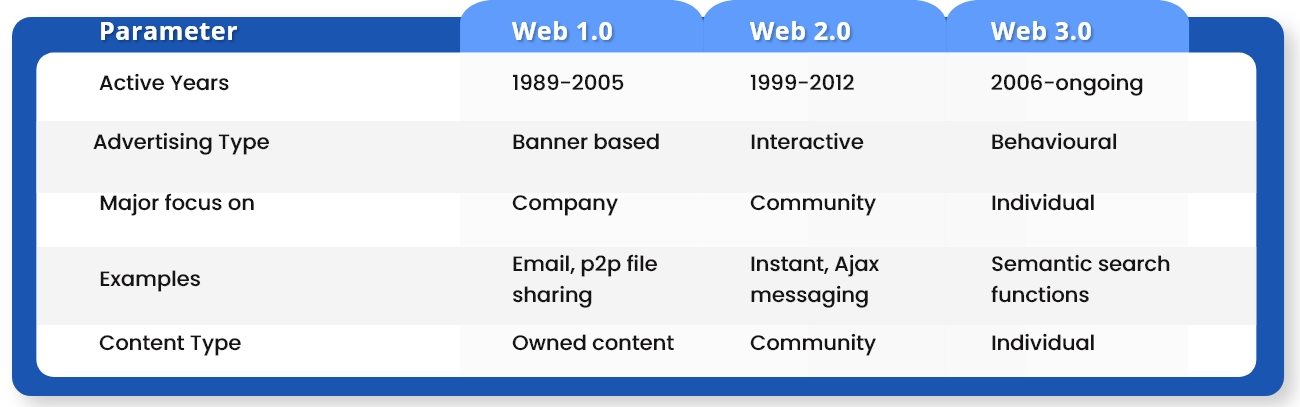
2. Difference between web 1.0, web 2.0 and web 3.0
3. Here are some of the main features of web 3.0
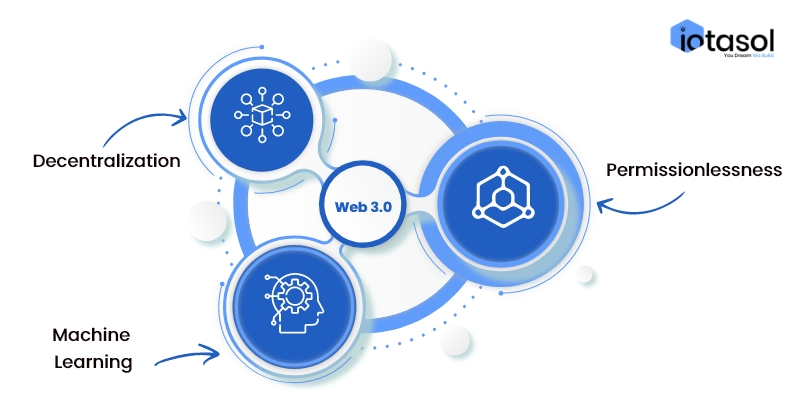

a. Decentralization
This is the major principle of web 3.0. Since web 2.0 depended on HTTP (a unique web address) to locate the information, which is placed at a fixed location, mostly on a single server.
However in web 3.0, users will be able to exercise greater control. Now the data, rather than being stored in massive databases of companies like Google, Meta etc., will be decentralized. Owing to the fact, that information will be searched based on the content and can be stored in multiple locations.
b. Permissionlessness
Permissionlessness will be prevalent in web 3.0 as people will need to seek no permission from any trusted intermediary or a government body. Rather, the incorporation of blockchain and decentralized peer to peer networks will allow anyone to interact and participate without anyone’s permission.
c. Machine Learning
In web 3.0, Machine learning will allow computers to produce faster and more relevant search results.
The development of the idea of Semantic web is likely to equip computers with the ability to process natural language such that computers will be able to understand language just like humans.
4. Is web 3.0 worth the hype?

Web 3.0 is definitely worth the hype because Web 3.0 is ushering the world into a new digital era- an era of autonomy, decentralization and interconnectivity. It removes the dependence on a so called safe intermediary. It brings the ownership of the data to the user . It opens avenues of growth by allowing capitalization using 3D visuals, machine learning and artificial intelligence to produce faster and more accurate results.



